Web Assembly Intro Session - Presentation Script
Presentation Script that I wrote before doing Web Assembly introduction Session in my org
Date: - 08/07/2022 Time: 1.00 pm
Minute 1–7
Ok Good Afternoon,
I am Amuthan.
So, the session is about WebAssembly Introduction
First things first,
What is WebAssembly?
To be short and very precious, “It is another thing that runs on browser”,
We knew that Javascript powers web mostly. So why we need another language model to run in the browser.
Before this, let’s see how JS is compiled.
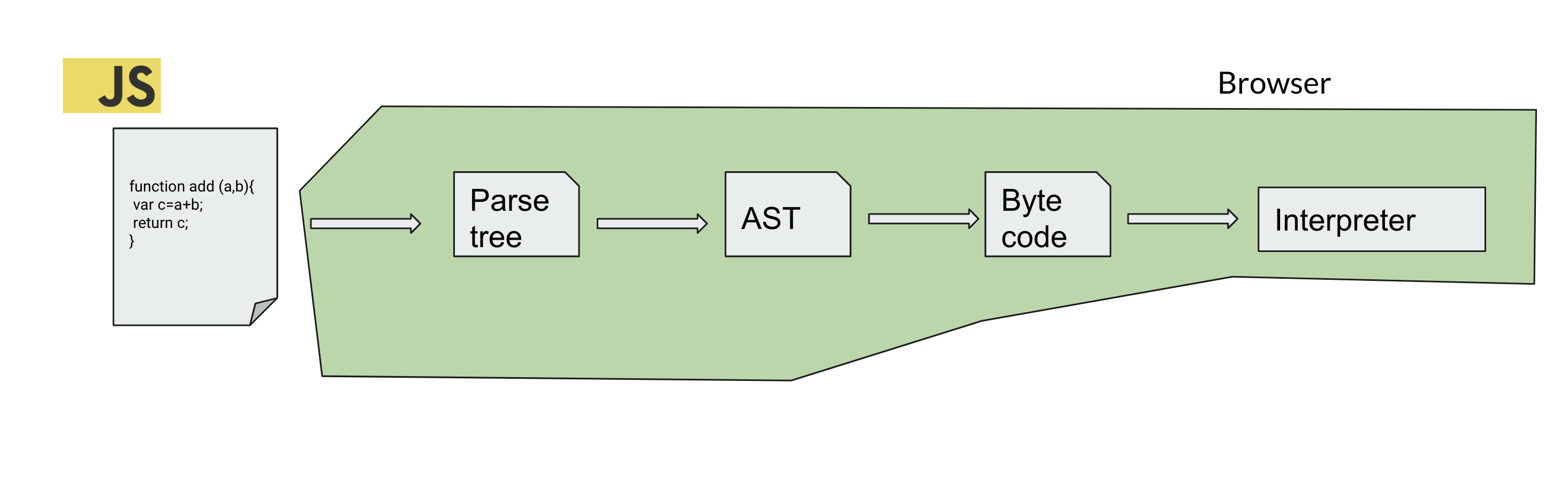
In terms of JS, after file is loaded from server, it will be tokenised, parsed and constructed in to the AST models, and byte code generation (for JIT compiler impl) will be done. Finally interpreter will execute the byte code. It is dynamically typed language, and expect to be interpreted. So the point is, this entire flow of compilation pipeline.
This pipeline exists for all of the language in the world. For example in java, we have JVM , which take Byte codes from class file, and runs it. Most of the time these are running on the server, or stand alone, so it can be compiled and it will be in a ready to run state. In browsers, it is not the case, we have the entire JS source code, and the compilation stage must be done on the browser itself. But Why?
We have lot of browsers, currently all of them agreed on common things such as HTML, CSS and obviously JS. You need to provide the JS file, and each browser engines have different implementation to execute the JS.
How about reducing the compilation states?. Let’s load the code, in some intermediate form, and execute it in the browser. So we all as a browser vendors, need to agree on this. That we compile our code, it can be in any language, but let’s bring close to ready to execute state. (as close to assembly) and load it in the browser. Let’s set some standard for that format. Finally WASM comes here.
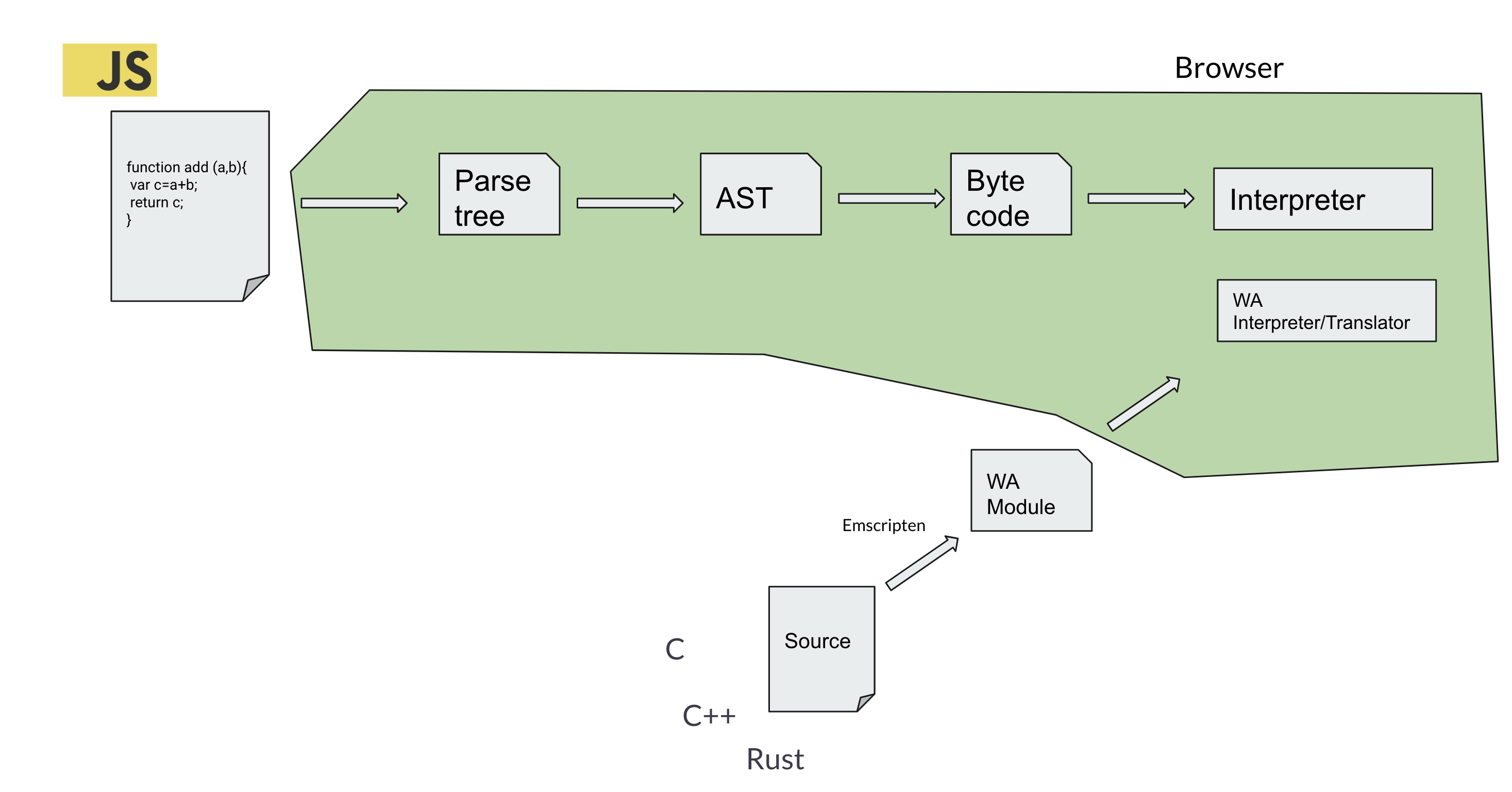
And it leads to this statement “Faster than Javascript”, We need to be very careful here that what we defines as Fast. It is not going to get magically faster, we will come on this later.
For to design any language, you have the idea of the environment it is going to run. Like JVM, it is a stack based machine, it has its own instruction set. And the instructions are designed in the way that , it will executed on that machine. Same like that web assembly, also defined the spec for the machine that it going to run. It is also a stack based machine, and has its own specifications. You can read later. But for web developers, we do not need to dig too much into that, having some idea on what it is that, how things are connected on certain level is enough.
Minute 7–12
Demo:
- Simple Addition Example [Explains: step by step, tell about Emscripten and compilation methods]
- Some running GAME app [Explains: Don’t need to explain in depth, but some overview]
- Benchmarking to show speed comparisons JS vs WA [Explains: Practically how fast is WASM, is it ok to choose for ordinary use cases]
But is this enough for conclude that JS is slower than WASM?. Of course not, this is not classic benchmarking. It is very small code, with some repetitive pattern. But real benchmarking should include lot of other real world code constructs.
Minute 12–14
Nuances behind choosing WA:
System Softwares → Let’s say you have a requirement for audio, video editing, or heavy signal processing logics, and dealing with 3D graphics, you can compile those code to WASM. But it is not that much easy, there are lot of things to consider. Like replacing OS specific calls with browser API calls for things like rendering images, and videos. In short it takes significant effort to achieve that.
Complex Algorithms that requires more number of steps → Or complex algorithms, that needs lot of steps for execution.
Questions from audience?
1) Why languages like C, C++, Rust are only spoken in terms of WASM?
These languages are almost don’t need any runtime requirements. If you compile Java to WASM, what about garbage collector? and other requirements. So strongly compiled languages are better suitable to these kind of cross targeting.